The healthcare industry has recently witnessed significant advancements with the introduction of medical robots. These robots are crucial in aiding healthcare professionals in treating medical conditions and optimizing hospital operations. Although the exploration of this technology began in the 1980s, it was in the 1990s that robots became an integral part of the surgical field. Since then, medical robots have diversified their functions, revolutionizing the healthcare sector. This article will highlight the primary types of medical robots that bring cutting-edge technologies to the field and contribute to improved interactions between healthcare providers and patients. Intrigued? Let’s start.
What are Medical Robots?
Medical robots, as their name implies, serve a vital role in medical settings. They are specifically engineered to execute precise movements that often surpass the capabilities of the human range of motion. These robots can remain with patients for extended periods as needed, providing continuous support. Additionally, they excel at automating mundane and repetitive tasks, enabling healthcare professionals to focus on more complex and high-level responsibilities. Listed below are the major types of medical robots introducing the latest technologies to the healthcare sector and enhancing the relationship between healthcare professionals and patients.
Types of Medical Robots
- Surgical Robots
- Robotic Rehabilitation Therapy (Pain Management)
- Service Robots in Hospitals (temi Robot, Double 3 Telepresence Robot)
- Social Robots (Pepper Robot)
- Robotics in Nursing
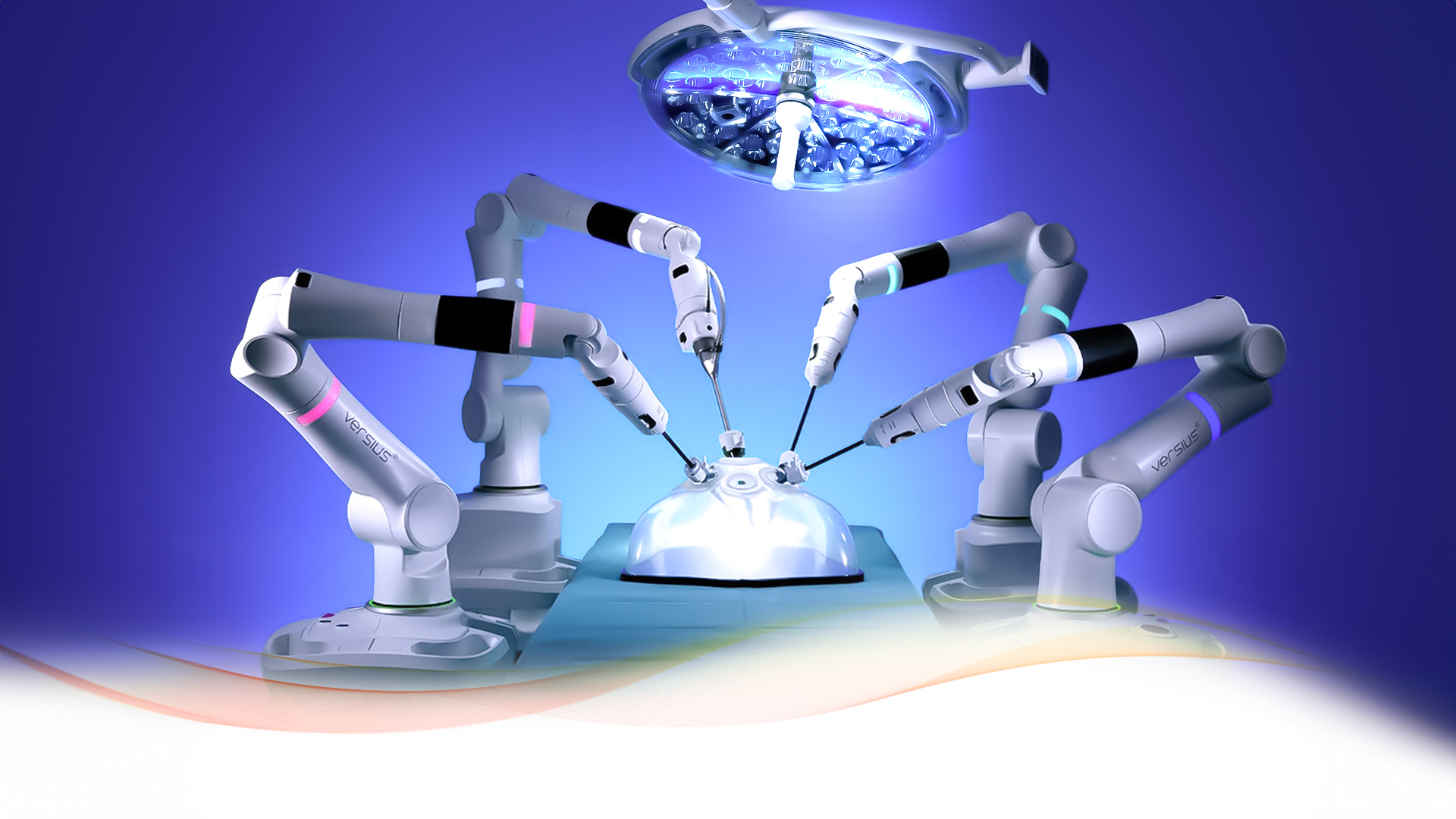
Surgical Robots
Robotic surgery or surgical robot assistants enables healthcare professionals or surgeons to perform many complicated invasive procedures with better precision, flexibility, and control. Minimally invasive surgery – surgery performed through small incisions – is typically associated with robotic surgery. In certain traditional open surgical procedures, it is also used.
One of the most prevalent clinical robotic surgical systems comprises a camera and mechanical arms with surgical instruments. Operating from a computer console positioned close to the operating table, the surgeon gains control over these arms. The console offers a high definition, magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical site, enhancing precision. While leading a team of assisting members, the surgeon orchestrates the operation seamlessly.
Examples of surgical robots include Intuitive’s Da Vinci platform, Vicarious Surgical’s Robotic System, and others.
Robotic Rehabilitation Therapy (Pain Management)
Advanced technologies are widely used in rehabilitation after surgeries or injuries. One such notable technologies include virtual reality pain management applications that allow the patient to immerse themselves into a virtual realm, ultimately distracting them from painful procedures. On the other hand, rehabilitation robots are advanced technological devices designed to aid individuals in their recovery journey after experiencing physical impairments, injuries, or neurological conditions. These robots are equipped with sophisticated sensors and actuators that assist patients in regaining strength, mobility, and motor functions.
By providing personalized and repetitive exercises, rehabilitation robots offer a controlled and safe environment for patients to engage in therapeutic activities. This innovative technology not only accelerates the rehabilitation process but also enhances patient motivation and engagement, leading to better outcomes in the recovery process. As rehabilitation robotics continues to evolve, these robots hold tremendous potential to transform the lives of countless individuals striving to regain their independence and improve their quality of life.
Examples of robotics in physical therapy include Burt Robot by Barret Technology, Myomo’s MyoPro Robot, etc.
Service Robots in Hospitals (temi Robot, Double 3 Telepresence Robot)
Service Robots like temi robots or Double 3 are widely used in healthcare settings to complete myriad tasks and streamline operations within the facility. These robots can use artificial intelligence and sensors to navigate their surroundings and interact with hospital staff members and patients. They can perform simple functions like assisting patients (especially the elderly) to connect with their doctors through teleconferencing, delivering food, transporting materials, or delivering supplies and medications to patients.
Social Robots (Pepper Robot)
Social humanoid robots, such as Pepper, offer valuable potential for deployment at the front kiosk of hospitals or care facilities, effectively engaging with patients and visitors, thereby alleviating the tedium of waiting periods. Their multifunctional capabilities extend to tasks such as soliciting visitor feedback, offering information about queries, and aiding regarding dining options or patient room, among other valuable functionalities. In addition, Pepper has speech recognition in 15 languages and can identify basic emotions and human features. These specifics encourage closer relationships between Pepper and patients from varied socioeconomic levels.
Robotics in Nursing
According to the survey by InsightAce Analytic, the worldwide robotic nurse industry is expected to grow 17.07% to reach an astonishing $2,777.61 million by 2031.
In Japan, humanoid robots have been integrated into elderly care facilities for several years, serving as complementary healthcare assistants. In a progressive development, hospitals and healthcare institutions have begun to adopt nurse robots and other AI-driven healthcare tools. These innovative solutions encompass larger robotic machines that can efficiently undertake physically demanding tasks such as patient transportation. At the same time, more miniature interactive robots are adept at addressing issues of loneliness and sedentary tendencies prevalent among the elderly population.
Examples of robotic nurses include Robot Nurse Bear, Robot Dinsow, and many more.
In the End
With ongoing advancements in technology and continued research, we expect medical robots to play an even more significant role in the future of healthcare. They hold the potential to alleviate the burden on healthcare professionals, optimize resource allocation, and improve patient outcomes. However, it is essential to strike a balance between the human touch and technological advancements, ensuring that these robots complement the skills and expertise of medical personnel rather than replace the critical element of compassion and empathy in patient care.